C++ Template Default Typename
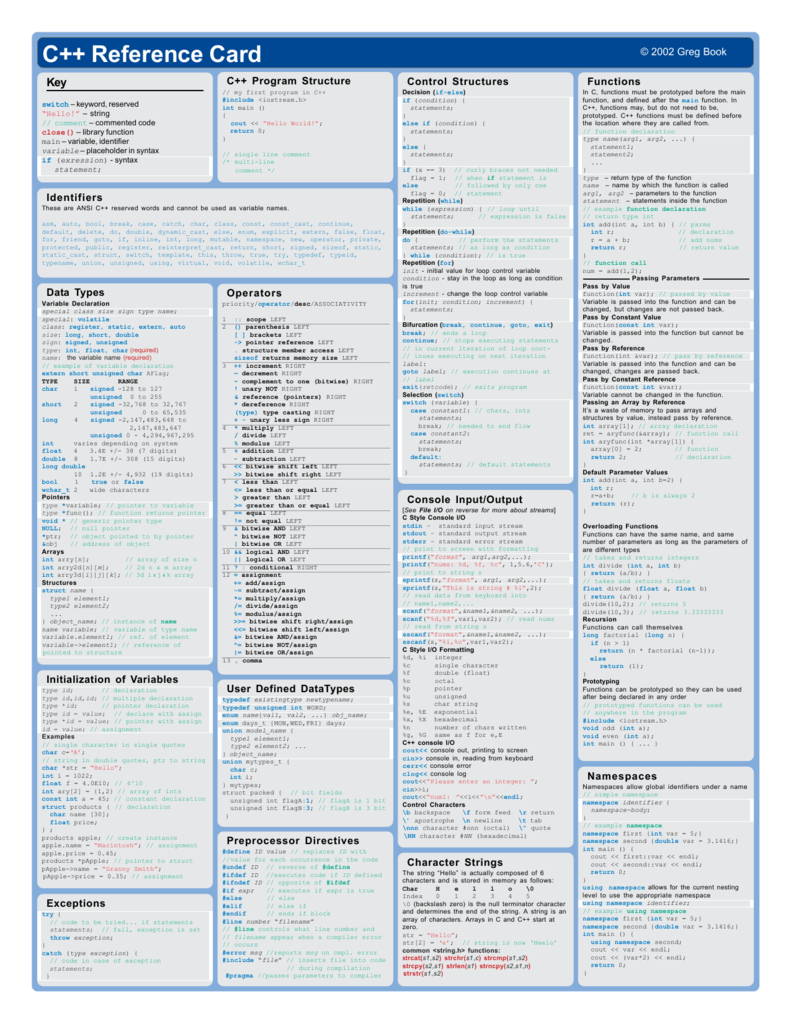
C++ template default typename - A class template can inherit all the constructors from a type argument if that type specifies a base class: Schmidt stl pair helper class • this template group is the basis for the map& set associative containers because it stores (potentially) heterogeneous pairs of data together • a pair binds a key (known as the first element) with an associated value (known as the second element) template <<strong>typename</strong> t, typename u. Template< typename t > class derived : Typename in a template template parameter: Template < typename t > constexpr t pi = t {3.141592653589793238462643383l}; The above range generator function generates values starting at start until end (exclusive), with each iteration step yielding the current value stored in start.the generator maintains its state across each invocation of range (in this case, the invocation is for each iteration in the for loop).co_yield takes the given expression, yields (i.e. When a template has a default argument you can leave it unspecified when you use it. By default, clang builds c++ code according to the c++14 standard. Class and function templates can have default arguments. // declare the constructors from t //.
But a slight addition helps catch cases where you're calling this function with template arguments that don't make sense (e.g. Float) or that would result in messy compiler errors (e.g. A function template starts with the keyword template followed by template parameter(s) inside <> which is followed by the function definition. Returns) its value, and suspends the. A deriving class can't inherit from multiple base classes if those base classes have constructors that have an identical signature.
C++ Insights simple example
A class template can inherit all the constructors from a type argument if that type specifies a base class: Template< typename t > std::string int_to_hex( t i ) { // ensure this function is called with a template parameter that makes sense. Template < typename t > constexpr t pi = t {3.141592653589793238462643383l};
C++ Reference Card.pmd
Template < typename t > constexpr t pi = t {3.141592653589793238462643383l}; Template< typename t > class derived : Templates in c++ is defined as a blueprint or formula for creating a generic class or a function.
c++ Page 3 MAlabdali
Template< typename t > class derived : Class and function templates can have default arguments. The above range generator function generates values starting at start until end (exclusive), with each iteration step yielding the current value stored in start.the generator maintains its state across each invocation of range (in this case, the invocation is for each iteration in the for loop).co_yield takes the given expression, yields (i.e.
C++ Templates. SFINAE
Class and function templates can have default arguments. // declare the constructors from t //. A class template can inherit all the constructors from a type argument if that type specifies a base class:
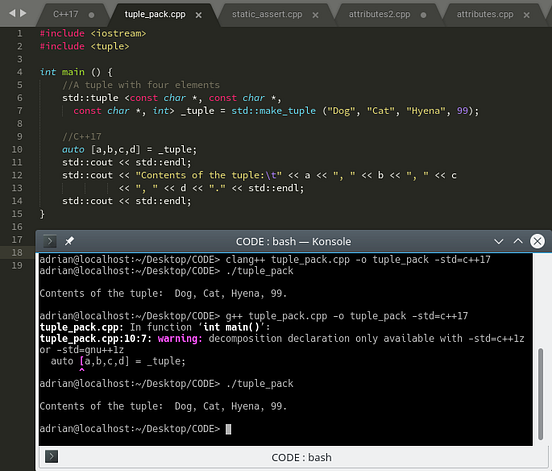
Modern C++ Part III New Language Features in C++17 by Adrian D
In a primary class template, the template parameter pack must be the final parameter in the template parameter list. The advent of c++11 automatic variable type deduction (auto) shifts the emphasis from the type name to the name of functions and members.thus, qpair, like std::pair and std::tuple, is mostly useful in generic (template) code, where defining a dedicated type is not possible. Template< typename t > class derived :
Class template with multiple parameters in c++ example
Templates in c++ is defined as a blueprint or formula for creating a generic class or a function. Returns) its value, and suspends the. Template< typename t > class derived :
Modern C++ Part III New Language Features in C++17 by Adrian D
A class template can inherit all the constructors from a type argument if that type specifies a base class: But a slight addition helps catch cases where you're calling this function with template arguments that don't make sense (e.g. Generic programming is an approach to programming where generic types are used as parameters in algorithms to work for a variety of data types.in c++, a template is a straightforward yet effective tool.
Solved Write In C++ Only Header File Heap.h //...
The c++ stl douglas c. Template <<strong>typename</strong> t> t functionname(t parameter1, t parameter2,.) { // code } in the above code, t is a template argument that accepts different data types (int, float, etc.), and typename is a keyword. Templates in c++ is defined as a blueprint or formula for creating a generic class or a function.
In a primary class template, the template parameter pack must be the final parameter in the template parameter list. The c++ stl douglas c. When a template has a default argument you can leave it unspecified when you use it. Class and function templates can have default arguments. Template< typename t > class derived : The above range generator function generates values starting at start until end (exclusive), with each iteration step yielding the current value stored in start.the generator maintains its state across each invocation of range (in this case, the invocation is for each iteration in the for loop).co_yield takes the given expression, yields (i.e. // declare the constructors from t //. By default, clang builds c++ code according to the c++14 standard. Float) or that would result in messy compiler errors (e.g. But a slight addition helps catch cases where you're calling this function with template arguments that don't make sense (e.g.
Templates in c++ is defined as a blueprint or formula for creating a generic class or a function. A deriving class can't inherit from multiple base classes if those base classes have constructors that have an identical signature. Returns) its value, and suspends the. Template < typename t > constexpr t pi = t {3.141592653589793238462643383l}; In a function template, the template parameter pack may appear earlier in the list provided that all following parameters can be deduced from the function arguments, or have default arguments: Typename in a template template parameter: Generic programming is an approach to programming where generic types are used as parameters in algorithms to work for a variety of data types.in c++, a template is a straightforward yet effective tool. Template< typename t > std::string int_to_hex( t i ) { // ensure this function is called with a template parameter that makes sense. Qpair's template data types (t1 and t2) must be assignable data types.you cannot, for example, store. A function template starts with the keyword template followed by template parameter(s) inside <> which is followed by the function definition.
Template <<strong>typename</strong> t> t functionname(t parameter1, t parameter2,.) { // code } in the above code, t is a template argument that accepts different data types (int, float, etc.), and typename is a keyword. Template<<strong>typename</strong> t, template<<strong>typename</strong>, int> class arr> class myclass2 { t t; Schmidt stl pair helper class • this template group is the basis for the map& set associative containers because it stores (potentially) heterogeneous pairs of data together • a pair binds a key (known as the first element) with an associated value (known as the second element) template <<strong>typename</strong> t, typename u. The advent of c++11 automatic variable type deduction (auto) shifts the emphasis from the type name to the name of functions and members.thus, qpair, like std::pair and std::tuple, is mostly useful in generic (template) code, where defining a dedicated type is not possible. A class template can inherit all the constructors from a type argument if that type specifies a base class: