C++ Template Specialization
C++ template specialization - For a class that also optimizes for space allocation and allows for dynamic resizing, see the bool specialization of vector (vector). A template has only one type, but a specialization is needed for pointer, reference, pointer to member, or function pointer types. It is returned by member function bitset::size. 19.1 template classes previous post 19.1 — template classes. C++11 introduced template aliases, which act like parameterized typedefs. If a primary template is a member of another class template, its partial specializations are members of the enclosing class template. Sometimes, the programmer may decide to implement a special version of a function (or class) for a given set of template type arguments which is called an explicit specialization. The specialization itself is still a template on the type pointed to or. If the enclosing template is instantiated, the declaration of each member partial specialization is instantiated as well (the same way declarations, but not definitions, of all other members of a template are instantiated). The result is a template parameterized on the remaining types.
Template < class t, class alloc = allocator > class vector; Explicit specialization may be declared in any scope where its primary template may be defined (which may be different from the scope where the primary template is defined; 19.3 function template specialization back to table of contents. The following code shows the definition of a template. // generic template vector just like arrays, vectors use contiguous storage locations for their elements, which means that their elements can also be accessed using offsets on regular pointers to its elements, and just as efficiently as in arrays.
HackerRank C++ Class Template Specialization solution
Explicit specialization may be declared in any scope where its primary template may be defined (which may be different from the scope where the primary template is defined; It is returned by member function bitset::size. The result is a template parameterized on the remaining types.
C++ Class Templates (Part 2) YouTube
The following code shows the definition of a template. Explicit specialization may be declared in any scope where its primary template may be defined (which may be different from the scope where the primary template is defined; The result is a template parameterized on the remaining types.
Class template with multiple parameters in c++ example
If the enclosing template is instantiated, the declaration of each member partial specialization is instantiated as well (the same way declarations, but not definitions, of all other members of a template are instantiated). 19.3 function template specialization back to table of contents. 19.1 template classes previous post 19.1 — template classes.
An introduction to C++ template programming
If a primary template is a member of another class template, its partial specializations are members of the enclosing class template. A template has only one type, but a specialization is needed for pointer, reference, pointer to member, or function pointer types. Template parameters n size of the bitset, in terms of number of bits.
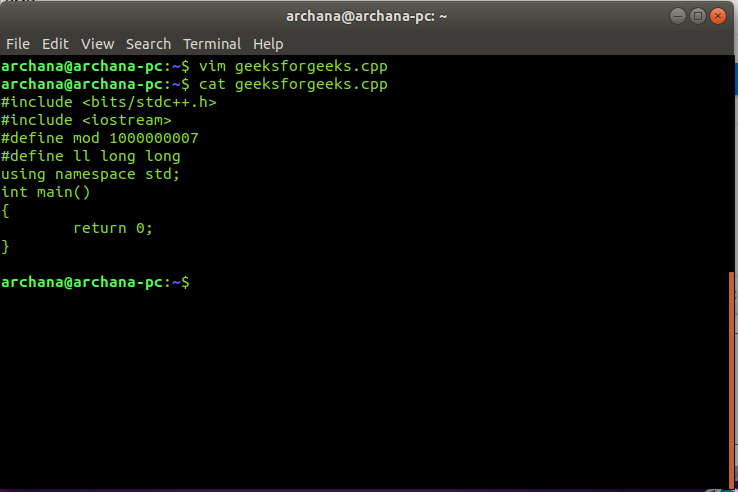
Creating a C++ template in vim in Linux
Template parameters n size of the bitset, in terms of number of bits. For a class that also optimizes for space allocation and allows for dynamic resizing, see the bool specialization of vector (vector). Sometimes, the programmer may decide to implement a special version of a function (or class) for a given set of template type arguments which is called an explicit specialization.
1.3 Standard Template Library STL and the game of Hex Coursera
Template parameters n size of the bitset, in terms of number of bits. It is returned by member function bitset::size. C++11 introduced template aliases, which act like parameterized typedefs.
Templates in C++
The result is a template parameterized on the remaining types. The following code shows the definition of a template. The specialization itself is still a template on the type pointed to or.
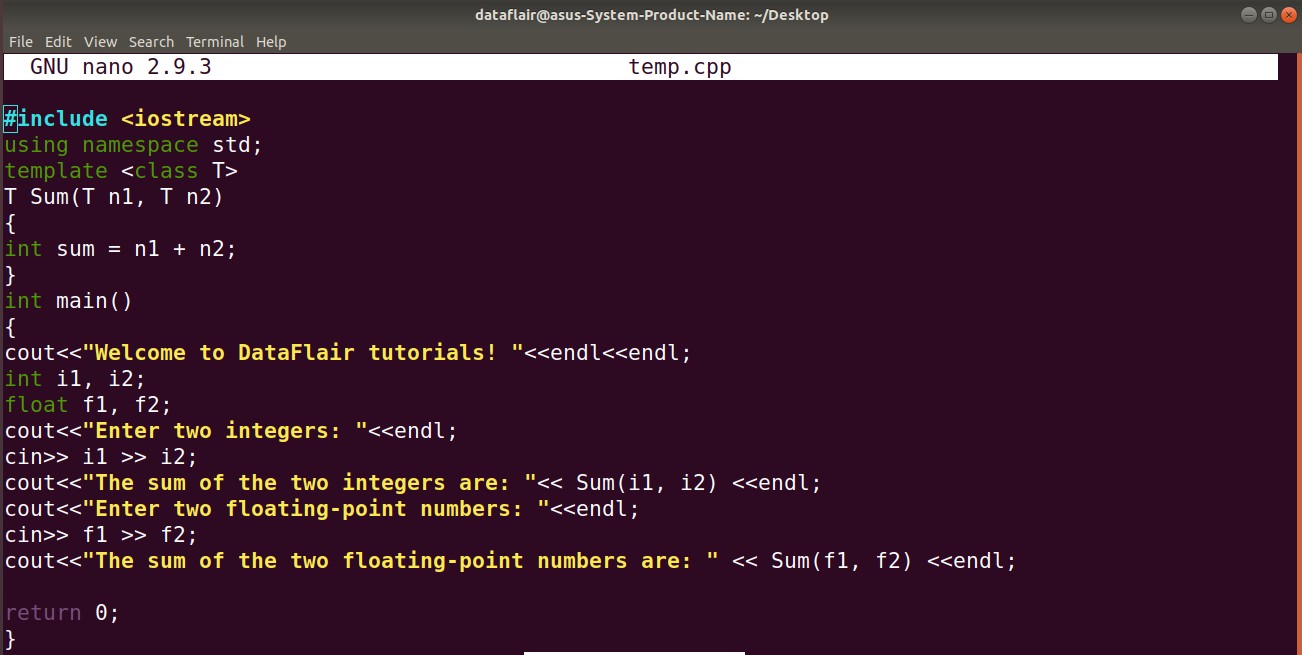
Cpp Template Function
The result is a template parameterized on the remaining types. 19.1 template classes previous post 19.1 — template classes. C++11 introduced template aliases, which act like parameterized typedefs.
If a primary template is a member of another class template, its partial specializations are members of the enclosing class template. Generic programming is an approach to programming where generic types are used as parameters in algorithms to work for a variety of data types.in c++, a template is a straightforward yet effective tool. The result is a template parameterized on the remaining types. The following code shows the definition of a template. // generic template vector just like arrays, vectors use contiguous storage locations for their elements, which means that their elements can also be accessed using offsets on regular pointers to its elements, and just as efficiently as in arrays. The specialization itself is still a template on the type pointed to or. 19.1 template classes previous post 19.1 — template classes. Template < class t, class alloc = allocator > class vector; C++11 introduced template aliases, which act like parameterized typedefs. A template has only one type, but a specialization is needed for pointer, reference, pointer to member, or function pointer types.
A template has multiple types and only some of them need to be specialized. If the enclosing template is instantiated, the declaration of each member partial specialization is instantiated as well (the same way declarations, but not definitions, of all other members of a template are instantiated). Template parameters n size of the bitset, in terms of number of bits. Sometimes, the programmer may decide to implement a special version of a function (or class) for a given set of template type arguments which is called an explicit specialization. 19.3 function template specialization back to table of contents. Consider the case where you want to design a class that stores 8 objects. Explicit specialization may be declared in any scope where its primary template may be defined (which may be different from the scope where the primary template is defined; For a class that also optimizes for space allocation and allows for dynamic resizing, see the bool specialization of vector (vector). Templates in c++ is defined as a blueprint or formula for creating a generic class or a function. It is returned by member function bitset::size.