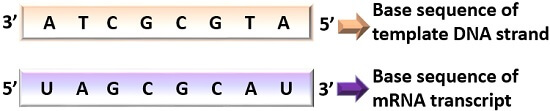
Template Strand Coding Strand
Template strand coding strand - The second coding region below is partial at the 3' end so > is used to indicate a 3' partial feature. The major technical challenges include various. Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil. Number of 1s in the template): The third example is of a 3' partial coding region on. Note that if the codon_start is not specified, then the software assumes a codon_start of 1. The field of study is based on the merging of. Molecular genetics often applies an investigative approach to determine the structure and/or function of genes in an organism's genome using genetic screens.
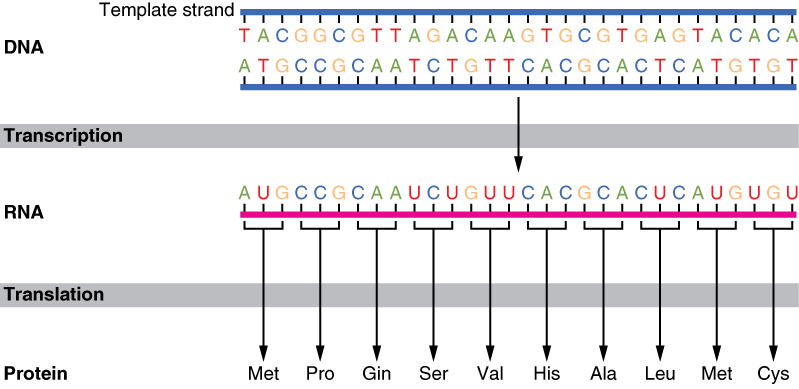
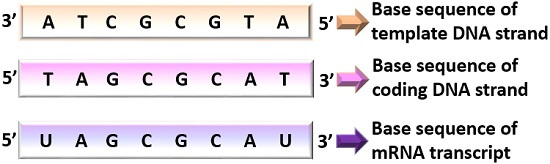
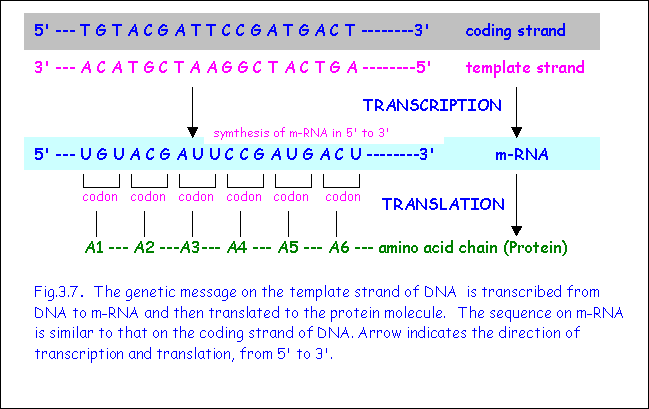
One dna strand (the template strand) is read in a 3′ to 5′ direction, and so provides the template for the new mrna molecule. The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (dna or rna sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins.translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger rna (mrna), using transfer rna (trna) molecules to carry. The 'coding' templates are based on the 110 pattern, although more 0s are required for most of. When the dna is read so that it can ultimately be translated into a protein, it can only be read in one direction. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein.
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Definition
Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination. The field of study is based on the merging of. Molecular genetics often applies an investigative approach to determine the structure and/or function of genes in an organism's genome using genetic screens.
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand (with Comparison Chart
The major technical challenges include various. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein.
The coding strand of DNA is 5'AATTCAAATTAGG3'
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (dna or rna sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins.translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger rna (mrna), using transfer rna (trna) molecules to carry. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. One dna strand (the template strand) is read in a 3′ to 5′ direction, and so provides the template for the new mrna molecule.
A promoter and terminator are present in which strand coding or
This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil. The third example is of a 3' partial coding region on. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein.
2
Molecular genetics often applies an investigative approach to determine the structure and/or function of genes in an organism's genome using genetic screens. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil.
Comparison Between Transcript Coding And Template Coding And
Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination. Require two words for extension: The field of study is based on the merging of.
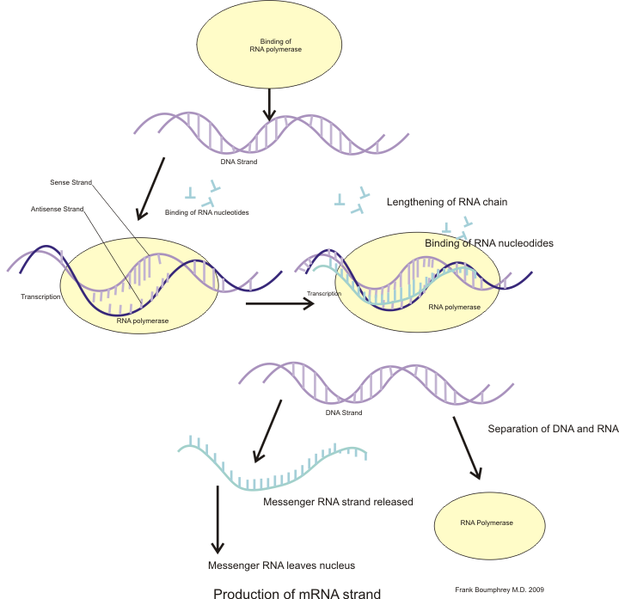
DNA Transcription Part1
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (dna or rna sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins.translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger rna (mrna), using transfer rna (trna) molecules to carry. One dna strand (the template strand) is read in a 3′ to 5′ direction, and so provides the template for the new mrna molecule. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand.
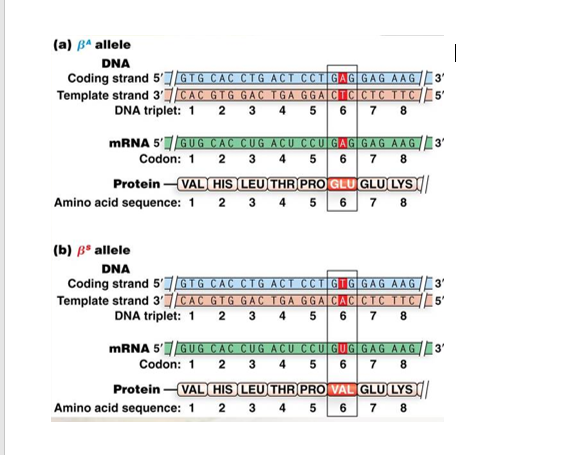
Solved (a) β^ Allele DNA Coding Strand 51 Template Strand...
In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein. The 'coding' templates are based on the 110 pattern, although more 0s are required for most of. Require two words for extension:
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand (with Comparison Chart
The second coding region below is partial at the 3' end so > is used to indicate a 3' partial feature. The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (dna or rna sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins.translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger rna (mrna), using transfer rna (trna) molecules to carry. When the dna is read so that it can ultimately be translated into a protein, it can only be read in one direction.
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Compare the Difference
One dna strand (the template strand) is read in a 3′ to 5′ direction, and so provides the template for the new mrna molecule. Require two words for extension: The field of study is based on the merging of.
The second coding region below is partial at the 3' end so > is used to indicate a 3' partial feature. Number of 1s in the template): Note that if the codon_start is not specified, then the software assumes a codon_start of 1. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. One dna strand (the template strand) is read in a 3′ to 5′ direction, and so provides the template for the new mrna molecule. Molecular genetics often applies an investigative approach to determine the structure and/or function of genes in an organism's genome using genetic screens. Require two words for extension: Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil. The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (dna or rna sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins.translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger rna (mrna), using transfer rna (trna) molecules to carry.
The third example is of a 3' partial coding region on. The field of study is based on the merging of. The major technical challenges include various. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein. The 'coding' templates are based on the 110 pattern, although more 0s are required for most of. When the dna is read so that it can ultimately be translated into a protein, it can only be read in one direction.